

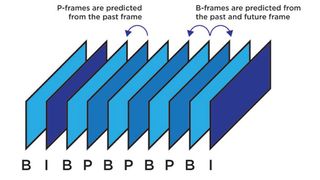
It’s a trade-off between quality and playback experience, with lossy codecs offering much smoother playback that might include interpolation and other compression artifacts. During playback, lossless codecs completely reconstruct the compressed data while lossy codecs serve up only an approximation. But out of all of them, H.264 and H.265 get the most attention by far.Ĭodecs come in two classes: lossless and lossy. MPEG-2, JPEG2000, and VP9 are just a few you might hear about. There are lots of different video codecs out there. The codec comes into play at the start, determining how the raw footage and sound are compressed within the container, and decodes the file for playback as needed. The difference is this: A container holds the compressed video and audio and any other components of the file, such as any metadata or subtitles. For video files, that means formats like AVI, MOV, or MP4. Bit Rate Compression Digital Video Tom Scott YouTube. The term itself is a combination of the words “coding” and “decoding.”Ĭodecs are often confused with containers. Tom Scott gives a superb demonstration of the factors affecting digital video quality. There are also audio codecs that do the same for audio. During the video compres-sion, the reconstructed geometry may suffer severe quality degradation due to the quantization errors. But what even is a “codec”?Ī video codec is a process for compressing and decompressing video data. It’s a term you’ll hear often in the streaming world and probably use a fair bit yourself. H.265: Average bandwidth required per resolution But the shift from macroblocks to CTUs is the most significant contributor to H.265’s greater efficiency. There are other technological enhancements at work, such as superior motion compensation and spatial prediction. So, whenever there's a fast movement in a game, like turning or running, there are some artifacts/pixelation that show up and the second I stop moving they go away and my video looks clear again. H.265 uses a newer block structure called coding tree units (CTUs), which can process sizes of up to 64×64 pixels. It seemed to exaggerate the pixelation from the artifacts as well, which isn't good for when I edit these videos in the long run either. H.264 uses what are called macroblocks, processing units that span 4×4 to 16×16 pixels. Whether you watch HBO through your cable/satellite box, stream Game of Thrones through HBO’s streaming apps HBO Go or HBO Now, or stream HBO through a Hulu, Sling TV, or. What accounts for this difference is how each video compression standard processes frames. This is a big advantage especially when it comes to storing and streaming 4K video and other high-resolution video content. The benefits of this are twofold: H.265 video files don’t take up as much storage space, and they require less bandwidth to stream. The H.265 codec compresses information more efficiently than H.264, resulting in files of comparable video quality that are about half the size.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
